Bodyweight training is a popular and accessible method. It offers an effective approach to improving strength, endurance, and flexibility without complex equipment. Whether you're an experienced athlete or a beginner looking to build strength, this method offers remarkable flexibility and effectiveness.
In this article, we'll explore the different aspects of bodyweight training, its benefits, the most effective exercises, and best practices for getting the most out of this method.
What is bodyweight training?
Bodyweight training involves using your own body weight as resistance to perform physical exercises. Unlike traditional training with free weights or machines, there's no need to invest in expensive equipment or visit a gym. The goal is to maximize strength, flexibility, and fitness by relying solely on the body's natural resistance.
The exercises are generally simple and can be done anywhere. It's this accessibility that makes bodyweight training attractive to many people.
The Benefits of Bodyweight Training
Bodyweight training has many benefits, both physically and mentally. According to a study published in BMC Sports Science, Medicine & Rehabilitation, physical training can have positive effects on mental health (1). This highlights not only the physical benefits, but also the mental impact of exercise. Here are some of the main benefits:
- Accessibility and convenience: As mentioned earlier, you don't need any special equipment to practice bodyweight training. This type of exercise is therefore accessible to everyone, regardless of their means or location. Just find a space to move and you're ready to begin.
- Functional Strength Development: Bodyweight exercises are particularly effective for functionally strengthening muscles. This improves performance in everyday tasks, such as lifting objects, and increases endurance.
- Improved core stability and flexibility: Certain exercises, such as planks and squats, are particularly beneficial for improving core stability. A strong core is essential for posture, mobility, and injury prevention.
- Improved cardiovascular fitness: Certain bodyweight exercises, such as burpees or hill sprints, are also effective at improving cardiovascular health by increasing heart rate. This combination of resistance training and cardiovascular work is ideal for those looking to improve their overall endurance.
- Injury Prevention: Unlike some intensive training methods, bodyweight training minimizes the risk of injury due to the lack of heavy loads and the focus on natural movement patterns.
The Best Exercises for Effective Bodyweight Training
Bodyweight training relies on simple yet powerful movements that can strengthen your entire body without the need for equipment. Here's a selection of effective exercises for each muscle group. Whether you're a beginner or more advanced, you can adjust the intensity to your level and progress at your own pace.
Push-ups: Strengthen your upper body
Push-ups are one of the most classic bodyweight exercises. They activate multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including the pectorals , triceps , shoulders , and core stabilizing muscles.
Basic exercise - classic push-ups:
- Description: Place your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, then lower your body until your chest almost touches the floor. Push back up, keeping your core straight.
- Tip: To avoid possible wrist injuries, make sure you position your hands correctly and don't let your elbows extend too far out from your body.
Beginner variation - push-ups on the knees:
- Description: If traditional push-ups are too difficult at first, try knee push-ups. By placing your knees on the floor, you reduce the load on your upper body while maintaining effective muscle activation in your pectorals, triceps, and shoulders. This version allows you to gradually work on technique and strength.
- Benefit: By mastering this variation, you gradually build strength and stability, making it easier to transition to regular push-ups when you feel ready.
Push-ups, beyond their effectiveness for upper body strength, also help maintain good core stability , which improves overall posture and prevents lower back pain.
Squats: Strengthen the legs
Bodyweight squats are a must for toning your legs and glutes . This active movement primarily targets your quadriceps , hamstrings , and glutes . It also helps strengthen the stabilizing muscles around your knees, ankles, and pelvis.
Traditional squat:
- Description: Stand straight with your feet hip-width apart. Lower yourself by bending your knees, keeping your back straight, until your thighs are parallel to the floor (or as low as you can reach without compromising posture).
Advanced Variation - Sumo Squats:
- Description: Place your feet wider than shoulder-width apart, with your toes pointed slightly outward. Lower into a squat as you would a standard squat, but with a more open hip angle. This variation works your adductors and glutes more.
- Advantage: This allows you to diversify your training and activate new muscle groups.
Squats are great for increasing functional strength and balance, while reducing the risk of knee injuries.
Lunges: A unilateral exercise for balancing strength
Lunges are a great exercise for working each leg independently. They primarily target the quadriceps , glutes , and hamstrings , while also engaging the stabilizing muscles of the knees and core .
Walking slots:
- Description: Step one foot forward in front of you, then lower your body until both knees form a 90° angle. Return to standing and repeat with the other leg. Repeat the movements, alternating legs.
Walking lunges are particularly effective for improving balance, coordination, and hip stability, in addition to strengthening leg muscles.
The core: Visible abs and a strong core
Core strengthening is a fundamental exercise that not only works the abdominals , but also the lumbar muscles and shoulders , contributing to better posture and a reduction in the risk of injury in daily life.
Plank :
- Description: In a push-up position, place your forearms on the floor and keep your body straight, forming a straight line from your head to your heels. Keep your glutes neither too low nor too high to avoid putting too much pressure on your lower back.
- Tip: Breathe calmly and hold the position for as long as possible. If you're just starting out, start with 20-30 second sessions and gradually increase.
Side plank:
- Description: Lie on your side, resting on one forearm and the outer edge of your foot. Raise your hips so that your body forms a straight line from head to toe. Hold this position by contracting your obliques and abdominals .
- Benefit: The side plank is great for strengthening the obliques , which are essential for core stability and balanced posture.
These core variations, especially when incorporated into a regular workout routine, help strengthen the core and improve overall posture, creating a solid foundation for other functional exercises.
Burpees: A Complete Exercise for Strength Training and Cardio
Burpees are an intense exercise that combines both strength training and cardio . They engage the entire body, including the arms , legs , and core , and are great for improving strength , endurance , and cardiovascular fitness .
Description :
- Execution: Start in a standing position. Jump down to place your hands on the floor and land in a plank position with your arms straight and your body straight. Then, quickly bring your feet back under your hips, then explosively jump back to standing, raising your arms overhead.
- Benefit: Burpees are a great way to train multiple muscle groups simultaneously while improving cardiovascular fitness.
Burpees increase workout intensity, burn calories, and improve overall endurance, making them a must-do exercise for those looking to tone up quickly.
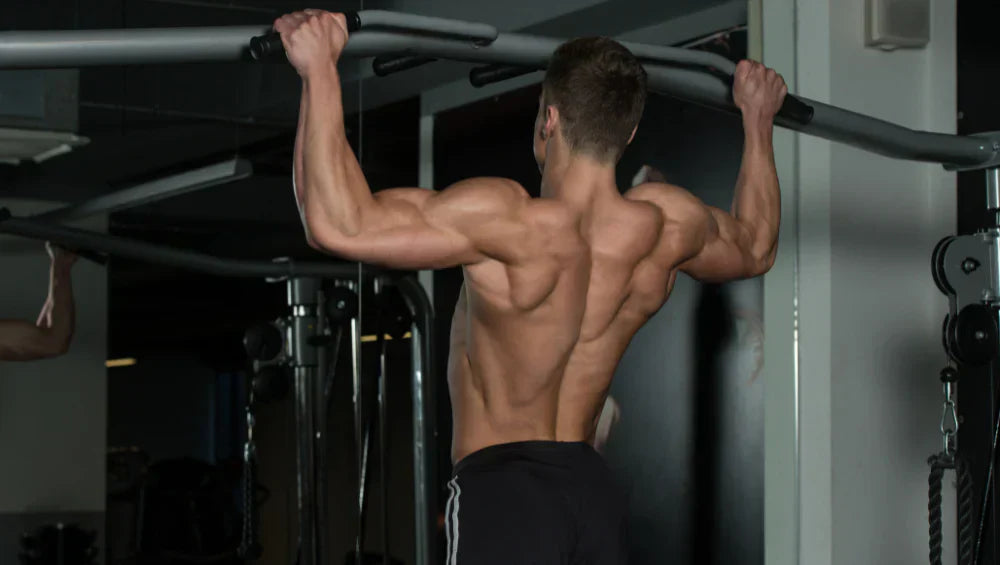
Pull-ups: For a strong upper body
Pull-ups are great exercises for working the upper body, especially the back, biceps, and shoulders.
Description :
- Execution: Hold onto a horizontal bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Pull yourself up until your chin is above the bar, then slowly lower yourself back to the starting position.
Pull-ups are particularly effective for developing back and arm strength while improving grip and coordination.
Dips: Tone the triceps and chest
Dips are a great exercise for working the triceps , pecs , and shoulders . They can be performed on a parallel bar or bench.
Description :
- Execution: Place your hands on a bench or bar and lower your body by bending your elbows. Once your arms are at 90 degrees, push through your hands to return to the starting position.
Dips specifically strengthen the upper body , with an emphasis on the arm and chest muscles.
Bodyweight Training Program: Total Body Strengthening
This workout program is designed to effectively strengthen your entire body, with a particular focus on your upper body, legs, and core. This program combines strength training and core exercises to improve strength, endurance, and stability. The workout is structured into circuits to work smoothly and continuously while maintaining a good intensity.
Instructions :
- Warm-up: Before you begin, do 5 to 10 minutes of light warm-up (such as brisk walking, jumping rope, or joint rotations).
- Rest time: Between each set, rest 60 to 90 seconds to allow for proper recovery.
- Progression: If an exercise becomes too easy, increase the repetitions or sets, or reduce the rest time.
| Exercise | Series | Rehearsals | Rest time |
| Classic pumps | 4 | 12-15 | 60-90 seconds |
| Traditional squats | 4 | 15-20 | 60-90 seconds |
| Walking lunges | 3 | 12 per leg | 60-90 seconds |
| Sheathing (plank) | 3 | 30-45 seconds | 60-90 seconds |
| Burpees | 3 | 10-12 |
90 seconds |
| Pull-ups (if possible) | 3 | 6-8 |
90 seconds |
| Bench Dips | 3 | 10-12 | 60-90 seconds |
Additional recommendations:
- Frequency: Perform this program 3 to 4 times per week for optimal strength and endurance development. You can also alternate this program with active recovery days, such as walking, to allow your muscles to recover.
- Recovery: Be sure to stretch thoroughly after each session to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
By following this training program, you will be able to develop your strength, improve your overall fitness and tone your muscles without additional equipment, while respecting the principle of body weight.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Neglecting technique: Maintaining good technique is essential for progress and avoiding injury. Each movement must be executed with precision to maximize muscle benefits while preventing excessive stress on the joints. Poor form can slow your progress and cause long-term pain.
- Ignoring the warm-up: Many people neglect to warm up, which increases the risk of muscle and joint injuries. A proper warm-up helps prepare your muscles and increase blood circulation before exercise.
- Overdoing reps: It's tempting to aim for high reps, but this can hinder your progress. The focus should be on quality of movement rather than quantity. Good technique, even with fewer reps, will always be more beneficial than fast, incorrect execution, which risks creating muscle imbalances or injuries.
- Ignoring nutrition: A balanced diet, including quality protein , complex carbohydrates like oats , and healthy fats , is essential to support physical exertion and promote recovery. As a supplement, BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) can help prevent muscle breakdown during training, while whey protein is a great way to ensure adequate protein intake for muscle repair after exercise. Proper nutrition optimizes your performance and speeds up recovery.
Conclusion :
Bodyweight training is an effective, accessible, and flexible method for improving overall fitness. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced athlete, you can tailor the exercises to your level and see impressive results. By incorporating exercises like push-ups, squats, and planks into your routine, you can improve your strength, flexibility, and posture, while reducing the risk of injury.
Remember, the key is to progress at your own pace, respect your body, and make sure each movement is performed correctly.
Source :
- Eather, N., Wade, L., Pankowiak, A., Eime, R. (2023). The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the 'Mental Health through Sport' conceptual model. BMC Sports Science, Medicine & Rehabilitation. DOI: https://systematicreviewsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13643-023-02264-8